Amberly Bossert, a behavior management specialist andour Sugar Land Clinical Director, gave an in-depth talk on basic behavior management principles at Dar-us-Sakina last month. Their 82 interns who work 1:1 with special needs students will use what they learned to help develop their tool kit when working with special needs students.
You can find the full recording of the presentation in the video here.
Key Essentials to Behavior Management and ABA Therapy
About ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis, commonly known as ABA therapy, represents a scientific and evidence-based methodology dedicated to understanding and enhancing human behavior. While it is particularly well-known for its effectiveness in treating individuals with autism spectrum disorder, ABA’s utility extends beyond this area. Its principles find application in various sectors including mental health, education, sports, and even animal training, demonstrating its wide-ranging applicability.
Why is ABA the Prime Choice for Parents of Children with Autism?
ABA is uniquely positioned as the only autism treatment endorsed by the United States Surgeon General and the American Psychology Association, highlighting its proven efficacy. In practice, Board-Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) are typically at the forefront of implementing ABA, ensuring a high standard of professional practice. ABA therapy often adopts a family-centered approach, not only engaging individuals but also working intimately with their caregivers. This approach can involve integrating additional therapeutic methods such as speech and occupational therapy, thereby providing a comprehensive treatment model.
The ABCs of Behavioral Management Techniques
A fundamental concept in behavior management is the ABCs of behavior. This framework consists of the Antecedent, the event or situation preceding a behavior; the Behavior itself, which is the observed action; and the Consequence, the outcome or result following the behavior. Recognizing these components is essential for understanding the underlying function of behavior, which is a critical step in developing effective strategies for behavior management.
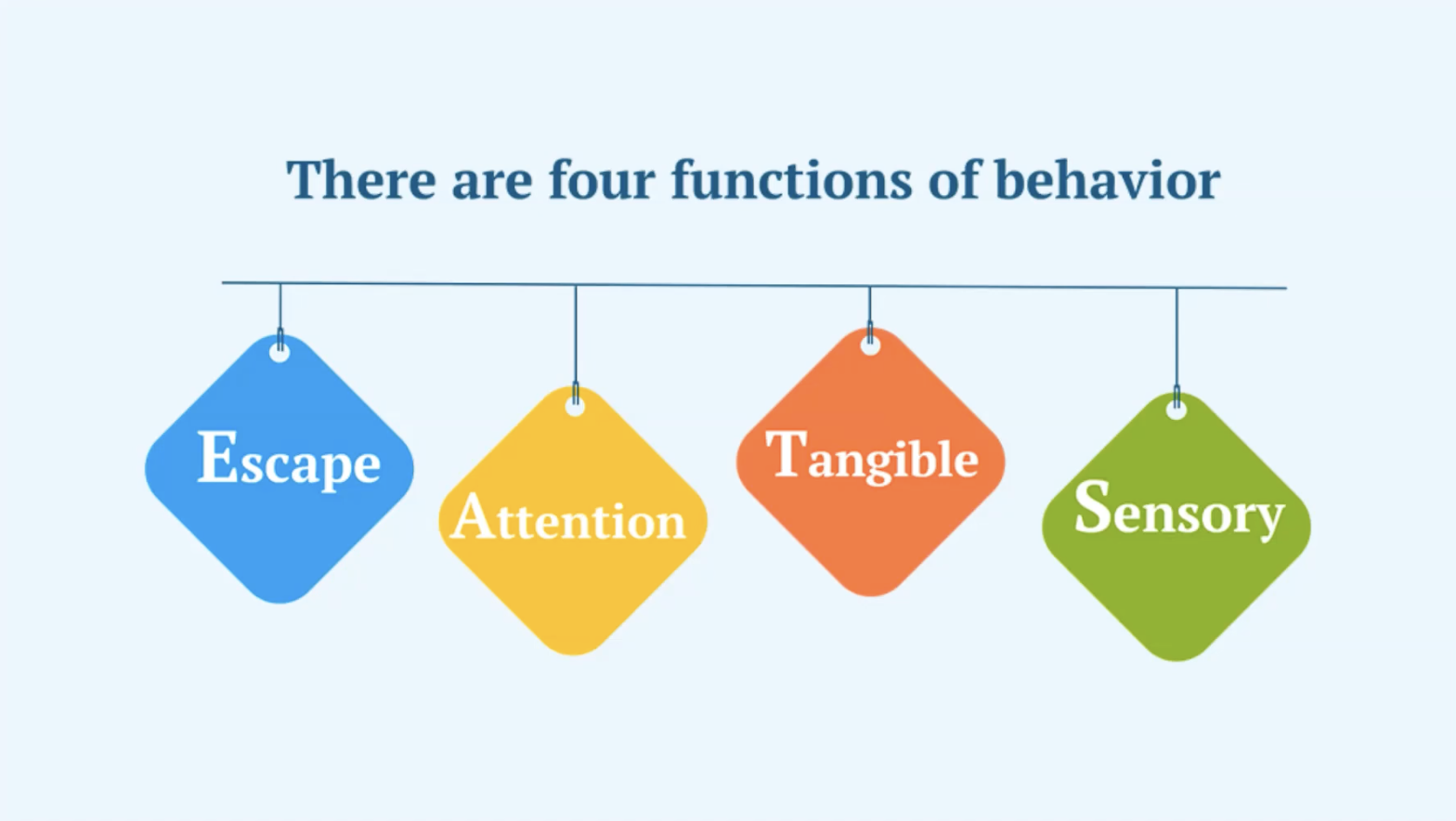
Functions and Management of Behavior
Every behavior serves a specific function or purpose, with these functions categorized as Escape, Attention, Tangible, and Sensory (or Automatic). Identifying the function behind a behavior is a pivotal aspect of creating targeted behavioral interventions. By applying real-world examples, professionals can illustrate how different antecedents and consequences influence behavior. This knowledge is instrumental in formulating behavior intervention plans, encompassing both preventive measures and responses to challenging behaviors. These plans are tailored to address the specific functions of behaviors, thereby enhancing the efficacy of behavior management techniques.
Negating Problematic Behavior with Behavioral Management Techniques
Preventing problem behaviors begins with establishing a positive rapport with students, as it sets a foundation for effective behavior management. Understanding the specific functions behind behaviors enables the development of tailored antecedent strategies. These can include offering choices to empower the students, utilizing visual schedules for clarity and predictability, and teaching functional communication to express needs appropriately.
Teaching and Reinforcing Replacement Behaviors
One essential strategy in behavioral management is to teach and reinforce replacement behaviors. These behaviors are more appropriate alternatives that fulfill the same function as the problematic behavior, without the negative consequences that problematic behavior can bring about. Continuous positive reinforcement of these replacement behaviors is crucial, as it promotes their recurrence and gradually diminishes the undesired behaviors.
Responses to Challenging Behaviors
Responding to challenging behaviors involves a range of strategies beyond punitive measures. Positive reinforcement, planned ignoring of undesirable behaviors, differential reinforcement, and the use of token economies are effective methods. Prompt intervention at the onset of a behavior can also be beneficial. Understanding an individual’s specific triggers and employing de-escalation techniques when necessary is key to managing these situations effectively.
Key Essentials to Behavior Management
Managing challenging behaviors encompasses a variety of strategies. Maintaining a calm and composed demeanor, using simple and clear language, and setting limits and choices can significantly influence behavior management. In instances of physical behaviors such as hitting or throwing objects, ensuring safety while avoiding further escalation is paramount. Adopting these strategies contributes to a more controlled and positive environment, conducive to learning and behavior improvement.
Effective Crisis Management within ABA Behavior Management Strategies
The first step involves identifying potential triggers and precursor behaviors to anticipate and mitigate crises. A comprehensive crisis management plan should outline specific strategies to be employed before, during, and after a behavioral incident. This plan includes assigning clear roles to team members, removing potential hazards to ensure safety, and applying de-escalation techniques to calm the situation.
Incident Reporting in ABA Therapy
Documenting each incident in detail helps in dissecting the ABCs of the behavior, evaluating the effectiveness of the strategies used, and identifying areas needing improvement. Regular analysis of these reports is invaluable for continuous learning and enhancement of behavior management practices.
The Importance of Collaboration and Teamwork in Crisis Situations
Handling behavioral crises effectively often requires teamwork and communication, not just within the immediate team but also with caregivers and other professionals involved in the individual’s care. Collaborative review and discussion of incident reports contribute to a deeper collective understanding.
Positive Relationships and Their Impact on Behavior Management
The foundation of effective behavior management lies in building positive and respectful relationships with students. Establishing rapport and understanding their individual preferences, dislikes, and triggers create a supportive and trusting environment. Such a relationship facilitates more effective behavior management, as students are more likely to respond positively in a nurturing atmosphere.
Effective Communication in Behavior Management
Clear and simple communication is a cornerstone of successful behavior management. Utilizing first-then language helps in setting clear expectations and reducing anxiety about upcoming activities. Visual aids like schedules and timers can also be invaluable in helping manage transitions and expectations, particularly for students who benefit from visual learning methods.
Attention Redirection and Reinforcement Techniques
Positive reinforcement is a powerful tool in encouraging the repetition of desirable behaviors. Consistently acknowledging and rewarding positive behaviors reinforces their value. Additionally, redirecting attention from problem behaviors to more constructive activities can effectively prevent behavioral escalations. This approach not only manages the immediate behavior but also teaches students alternative ways to channel their energy and attention.
Keeping a Calm and Controlled Environment for Education
The educator’s demeanor plays a critical role in behavior management. Maintaining a calm, composed, and consistent presence can significantly influence the classroom’s atmosphere, encouraging similar behavior in students. Strategies like taking walks or changing the scenery can be effective in managing behaviors, especially in situations where the environment may contribute to the student’s behavior. Ensuring a safe and controlled environment is paramount in effectively managing and improving student behavior.
How to Foster Functional Communication
Behavior management involves teaching students functional communication skills. These skills enable them to express their needs and desires effectively, thereby reducing the likelihood of problem behaviors arising from communication challenges. Additionally, incorporating activities that build skills like patience and appropriate ways to seek attention can significantly improve behavior management outcomes.
Applying Behavioral Interventions
Behavioral interventions such as differential reinforcement and token economies play a vital role in managing challenging behaviors. These strategies reward positive behaviors while minimizing attention to negative behaviors. Prompt interventions can also be crucial, offering solutions and support at the early signs of frustration or agitation, thus preventing escalation of behaviors.
Handling Physical Behaviors Safely
Managing physical behaviors such as hitting, biting, or throwing objects requires a focus on safety and prevention. It’s important to employ strategies that ensure the safety of all involved while avoiding actions that could escalate the situation. Responding appropriately and safely to these behaviors is essential in maintaining a secure and positive learning environment.
How to Customize Interventions for Individuals
Being flexible and adaptable in one’s approach, while considering the specific circumstances and triggers of each student, ensures that interventions are as effective and supportive as possible. Understanding and adapting to these individual differences is key to successful behavior management and student development.
Crisis Intervention in Behavioral Management
A well-defined crisis intervention plan is crucial, encompassing the identification of potential triggers, effective de-escalation techniques, and a clear understanding of each team member’s role during a crisis. Such planning ensures a coordinated and effective response to challenging situations.
Prioritizing Safety During Behavioral Crises
During a behavioral crisis, the safety of all individuals is paramount. This involves the removal of potential hazards and the implementation of clear guidelines for responding to physical aggression or self-injurious behaviors. Ensuring a safe environment during these challenging moments is essential for the well-being of everyone involved.
Learning, Post-Crisis Situation
After a crisis, it’s important to review and analyze the incident to better understand the triggers and the effectiveness of the responses used. This post-crisis analysis is a learning opportunity to refine and improve future crisis management strategies, thereby enhancing the overall approach to behavior management.
Collaboration in Crisis Management
A collaborative approach in managing crisis situations is invaluable. Involving caregivers, professionals, and team members in discussions and strategy development enhances the effectiveness of crisis management. Sharing insights and experiences among all stakeholders contributes to a more comprehensive and effective approach to handling behavioral crises.
Fostering a Supportive Learning Environment
A supportive learning environment is fundamental to effective behavior management. Creating a nurturing space that understands and accommodates individual needs can significantly enhance behavior management outcomes. Employing techniques like offering choices, using positive reinforcement, and adapting the environment to meet the specific needs of each student fosters a conducive atmosphere for learning and behavioral improvement.
Emphasizing Teamwork for Behavioral Management Success
Clear roles and responsibilities within a team are essential for managing behaviors effectively. Teamwork, characterized by strong collaboration and communication, ensures that everyone is on the same page, providing consistent support and intervention. This collaborative approach enhances the overall effectiveness of behavior management strategies.
Valuing Feedback and Adaptive Strategies
Regular feedback sessions are crucial in evaluating and refining behavior management strategies. Discussing challenges, successes, and potential improvements helps in adapting approaches to better suit individual student needs and progress.
Continuous Learning in Behavioral Management
Continuous learning and professional development are vital in the ever-evolving field of behavior management. Staying informed about the latest research, techniques, and best practices ensures that educators and behavior specialists are equipped with the most effective tools and knowledge. This commitment to learning is key to maintaining high standards in behavior management and student support.
Key Takeaways:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a versatile and evidence-based approach, effective in a wide range of settings, not just for autism.
- Understanding the ABCs of Behavior (Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence) is crucial in identifying the function of behavior and devising effective management strategies.
- Each behavior serves a function – Escape, Attention, Tangible, or Sensory – and recognizing this is key to developing targeted interventions.
- Preventive strategies and positive relationships are foundational in managing behavior, focusing on understanding individual needs and triggers.
- Teaching replacement behaviors that serve the same function as problematic behaviors, and reinforcing these, is essential in behavior modification.
- Crisis management plans should include strategies for each stage of a behavior and emphasize safety and de-escalation techniques.
- Incident reporting and analysis provide valuable insights for understanding behaviors and refining intervention strategies.
- A collaborative approach, involving teamwork and communication with caregivers and professionals, enhances the management of challenging behaviors.
- Adapting the learning environment and strategies to individual needs is crucial for effective behavior management.
- Continuous learning and professional development are essential for staying informed and effective in the field of behavior management.
If you’d like to know more about ABA therapy, behavioral management or anything else Autism-related, we’ve got you covered. Be sure to browse our parent resources and our Autism blog for valuable insights on parenting and otherwise interacting with those on the Autism spectrum.